Ch6. Counting¶
约 960 个字 预计阅读时间 3 分钟
The Pigeonhole Principle¶
- If \(k\) is a positive integer and \(k+1\) or more objects are placed into \(k\) boxes, then there is at least one box containing two or more of the objects.
- If \(N\) objects are placed into \(k\) boxes, then there is at least one box containing at least \(\lceil {\frac{N}{k}} \rceil\) objects.
- prased to terms of functions:
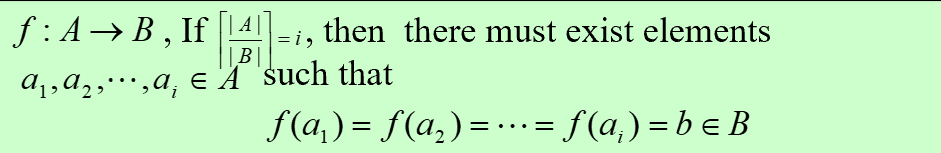
Ramsey Number¶
- Assume that in a group of 6 people, each pair is two friends or two enemies. Show that there are either 3 mutual friends or 3 mutual enemies
- Proof: 考虑 \(a_1\),剩下 5 个人分到 2 个坑(friend & enemy)里,至少有 \(\lceil \frac{5}{2} \rceil\) 个 friend 或 enemy
- Ramsey Number - \(R(m,n)\)
- \(m,n\ge 2\)
- \(R(m,n)\) 表示至少有 \(m\) 对朋友或者 \(n\) 对敌人的 最少人数
- \(R(m,n)=R(n,m)\)
- \(R(3,3)=6,\, R(4,4)=18 \,,R(2,n)=n,\, 7\le R(3,4)\le 9\)
Permutations¶
Circular Permutation¶
- A circular r-permutation of n people is a seating of r of these n people around a circular table, where seatings are considered to be the same if they can be obtained from each other by rotating the table. (\(\frac{A_n^r}{r}\))
- 当左右邻居相同也认为是相同排列时:\(\begin{cases} n& r=1\\ C_n^2& r=2\\ \frac{A_n^r}{2r}& r \ge 3\\ \end{cases}\)
Permutation with Repetiton¶
- r-permutation of a set with n elements, 即需要 \(r\) 个球,可重复 => \(n^r\)
- n-permutation with limited repetition, 即 \(n\) 个球,放入 \(k\) 个盒子,每个盒子分别放 \(n_1,n_2...n_k\) 个
- \(\frac{n!}{n_1! \cdot n_2!\cdot ...\cdot n_k!}\)
Generating Permutations¶
Next Permutation,其实是一种 Greedy
- 从排列的右端开始,找出第一个比右边数字小的数字的序号 \(j\)
- 在 \(P_j\) 的右边的数字中,找出所有比 \(P_j\) 大的数字中最小的数字 \(P_k\)
- 交换 \(P_j,P_k\)(保证大)
- 再将排列右端的递减部分 \(P_{j+1}, P_{j+2},…P_n\) 倒转,因为 \(j\) 右端的数字是降序,所以只需要其左边和右边的交换,直到中间,因此可以得到一个新的排列(逆序保证尽量小)
Binomial Theorem¶
- \((x+y)^n=\sum_{i=0}^nC_n^i\cdot x^{n-i}y^i\)
- 如果是多项式展开算系数 \((x_1+x_2+...+x_m)^n\),例如
- \((x + y + z)^{10} = (x^3y^2z^5) \cdot C(10, 3) \cdot C(7, 2)\)
Combinations¶
Simple Properties¶
- Pascal's Identity
- \(C_{n+1}^k=C_n^{k-1}+C_n^k\)
- \(r\le n\), \(C_{n+1}^{r+1}=\sum_{i=r}^nC_i^r\)
Combination with Repetiton¶
球盒模型 🔗
球、盒子均可分辨¶
- \(n\) 个球,\(k\) 个盒子,可空
- 每个球都有 \(k\) 种放法,即 \(k^n\)
- 若每个盒子分别放 \(n_1,n_2...n_k\) 个,则为 \(\frac{n!}{n_1! \cdot n_2!\cdot ...\cdot n_k!}\)
球可分辨、盒子不可分辨¶
- \(n\) 个球,\(k\) 个盒子,可空
- 组合出可能的情况,具体讨论;如 \(n=4,k=3\),有:
- 4 0 0 (1)
- 3 1 0 (4)
- 2 2 0 (3)
- 2 1 1 (6)
- PS: 注意等分组计算就 ok
- 可由第二类斯特林数(\(n\)放入\(k\), 非空)计算,定义 \(S(i,j)\)为\(i\)个球放入\(j\) 个盒子的方法数
- \(S(i,j)=S(i-1,j-1)+j\cdot S(i-1,j)\)
球不可分辨,盒子可分辨¶
- \(n\) 个球,\(k\) 个盒子,可空
- 相当于 r-combination (r 是球的个数) 问题,即球和隔板混选,\(C(r+k-1,k-1)\)
- 在这里,\(k-1\) 为隔板数,\(r\) 为球的个数
- 多项式 \((x_1+x_2+...+x_m)^n\) 的展开项数:\(C(n+m-1,m-1)\)
球、盒子均不可分辨¶
- \(n\) 个球,\(k\) 个盒子,可空
- 枚举出可能的情况,即分完组就 ok
- 也可由 dp 计算
Generating Combinations¶
- 出现/不出现,用位串的一位表示是否出现,列出所有位串即全组合
- 若将位串从小到大排列(按位串对应的无符号数的大小),那么生成「Next Combination」的做法是:
- 从右往左找到第一个 0,将其变为 1
- 从该位开始,从左往右将所有 1 置 0
Generating r-combination¶
- \(\{1,2,3,...,n\}\)
- \(S_1=\{1,2,...,r\}\),假设当前为 \(\{a_1,a_2,...,a_r\}\)
- 从左往右找最后一个 / 从右往左找第一个 \(a_i\neq n-r+i\),将其变为 \(a_i+1\),并将其之后的所有元素替换为 \(a_i+j-i+1\, \,(j=i+1,i+2,...,r)\)