Ch9. Relations¶
约 2232 个字 预计阅读时间 7 分钟
Binary Relation¶
- Definition: A binary relation \(R\) from a set \(A\) to a set \(B\) is a subset of \(A \times B\)
- \(R \subseteq A\times B\)
- \(R=\{(a,b)\mid a\in A, b\in B, aRb\}\)
Relation on a Set¶
- Definition: A relation on a set \(A\) is a relation from \(A\) to \(A\), a.k.a. a relation on a set A is a subset of \(A\times A\)
- \(R\subseteq A\times A\)
- How many binary relations are there on a set \(A\) with \(n\) elements? - \(2^{n^2}\)
Representing Relations¶
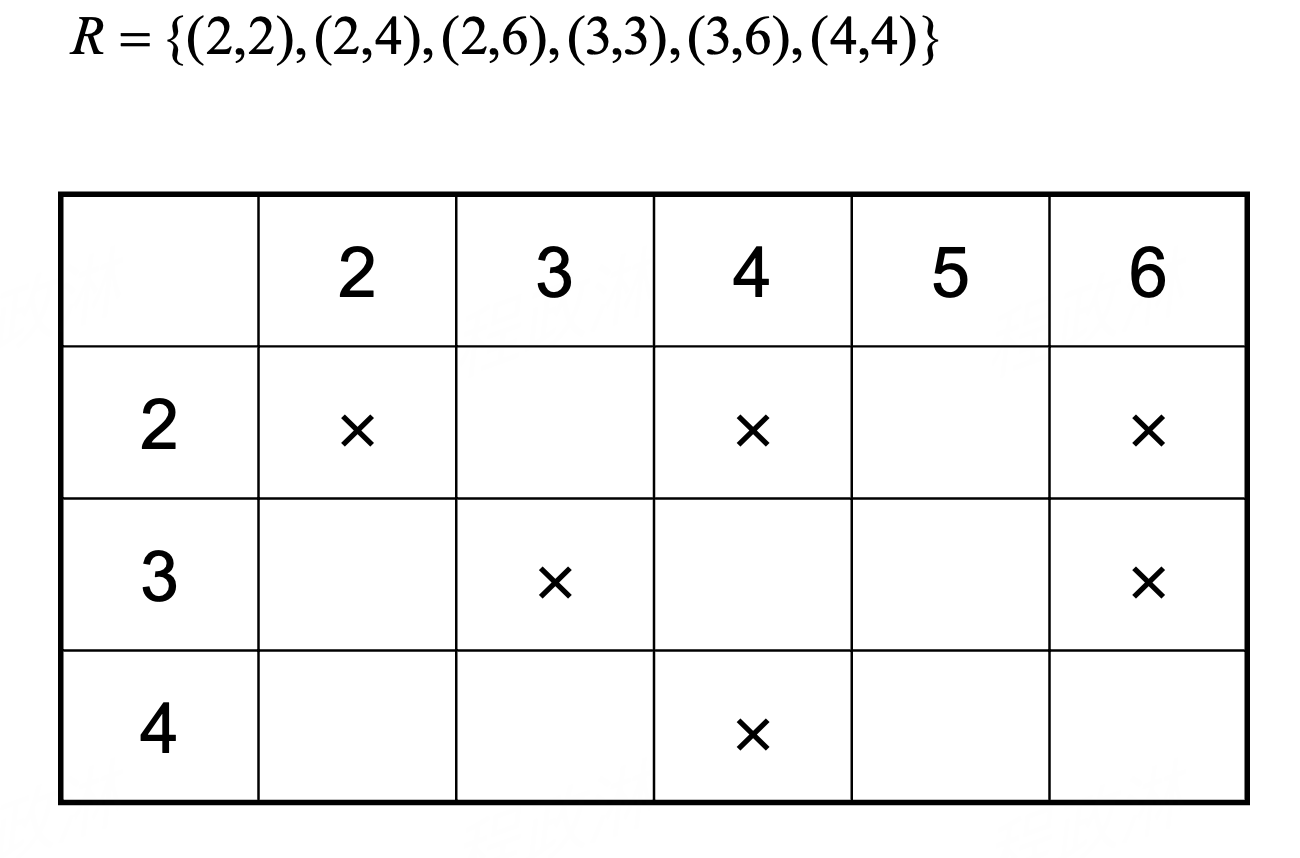
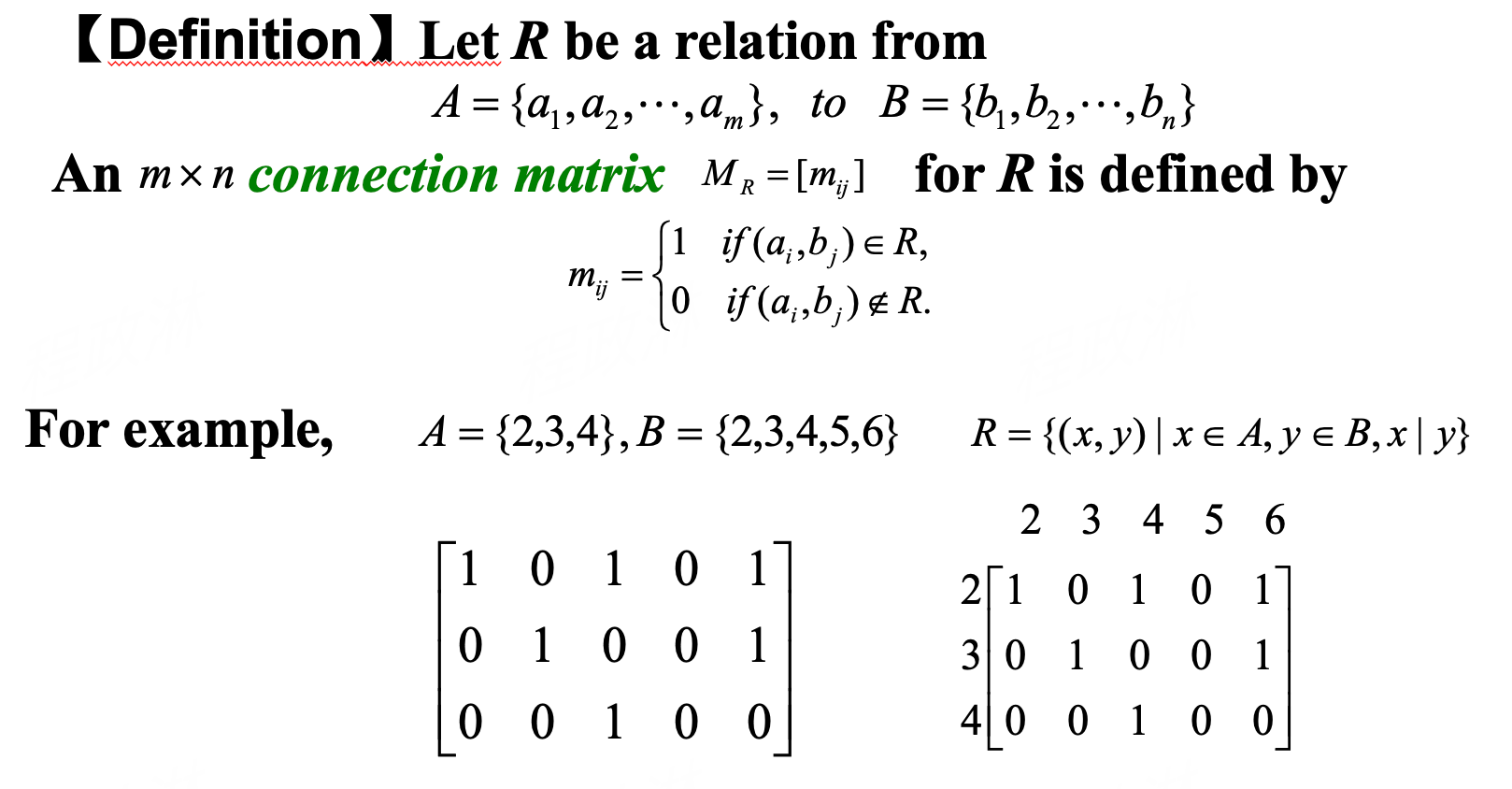
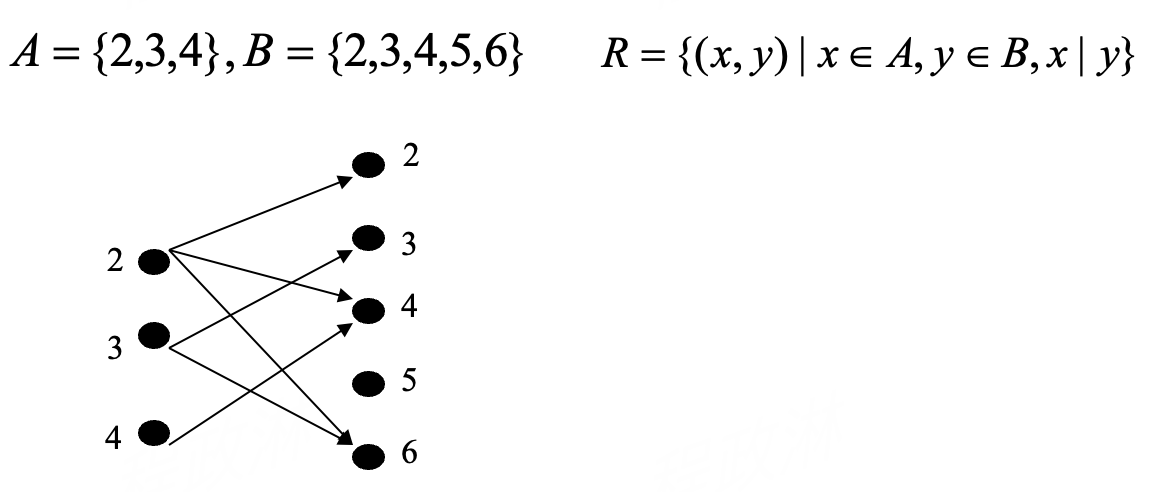
Special Properties of Binary Relations¶
若无特殊说明,在说明性质时,均是 \(n\) 元集上的关系
- Reflexive (自反)
- \((x,x)\in R\), for element \(x\in A\)
- \(\forall x(x\in A \to (x,x)\in A)\)
- 自反关系个数为:\(2^{n^2-n}\)
- Irreflexive (反自反)
- \(\forall x(x\in A \to (x,x) \not \in A)\)
- 反自反关系个数:\(2^{n^2-n}\)
- 一个关系可以既不是 reflexive 也不是 irreflexive,有 \(2^{n^2}-2\cdot 2^{n^2-n}\)
- \(R_1,R_2\) reflexive
- \(R_1 \cup R_2, R_1\cap R_2, R_1\circ R_2\) reflexive
- \(R_1 \oplus R_2,R_1-R_2\) irreflexive
- \(\forall x\forall y((x,y)\in R \to (y,x) \in R)\)
- 对称关系个数为:\(2^n\cdot 2^{\frac{n^2-n}{2}}=2^{\frac{n(n+1)}{2}}\)
- \(R^n\) 也是对称的
- \(\bar R\) 也是对称的
- \(\forall x\forall y((x,y)\in R \land (y,x) \in R \to x=y)\)
- \(\forall x \forall y ((x,y)\in R \land x\neq y \to (y,x)\not \in R)\)
- 非对称关系个数为:\(2^n\cdot 3^{\frac{n^2-n}{2}}\)
- 有 3 个选择,是 (0, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0)
- \(\forall x\forall y((x,y)\in R \to (y,x) \not\in R)\)
- 非对称关系个数为 \(3^{\frac{n^2-n}{2}}\)
- \(\forall x\forall y \forall z((x,y)\in R\land (y,z)\in R\to (x,z)\in R)\)
- \(\neg(m_{ij}\land m_{jk})\vee m_{ik}\)
Quoted from Wiki 🔗: No general formula that counts the number of transitive relations on a finite set is known
- We can find formula for reflexive & symmetric & transitive (equivalence relations) relations, which is \(\sum_{k=0}^nS(n,k)\), \(S(n,k)\) 是第二类斯特林数
- symmetric, transitive \(\not \Rightarrow\) reflexive!!!
Combining Relations¶
- \(A\) 到 \(B\) 的关系是 \(A\times B\) 的子集,任意两个 \(A\) 到 \(B\) 的关系也可以用集合运算符连接
- \(\cup, \cap,\oplus,-,\bar{}\)
Composition - \(S\circ R\)¶
- \(R=\{ (a,b) \mid a \in A, b\in B,aRb \},\, S=\{ (b,c) \mid b \in B, c\in C,bSc \}\)
- \(S\circ R = \{(a,c)\mid a\in A\land c\in C\land \exists b(b\in B\land aRb\land bSc\}\)
- \(S\circ R\neq R\circ S\)
- \(S \circ R = M_R\cdot M_S\)
- 如何计算?
- 按定义直接复合
- 关系矩阵做乘法
- \(R^n\) is defined by: \(R^1=R\), \(R^{n+1}=R^n\circ R\)
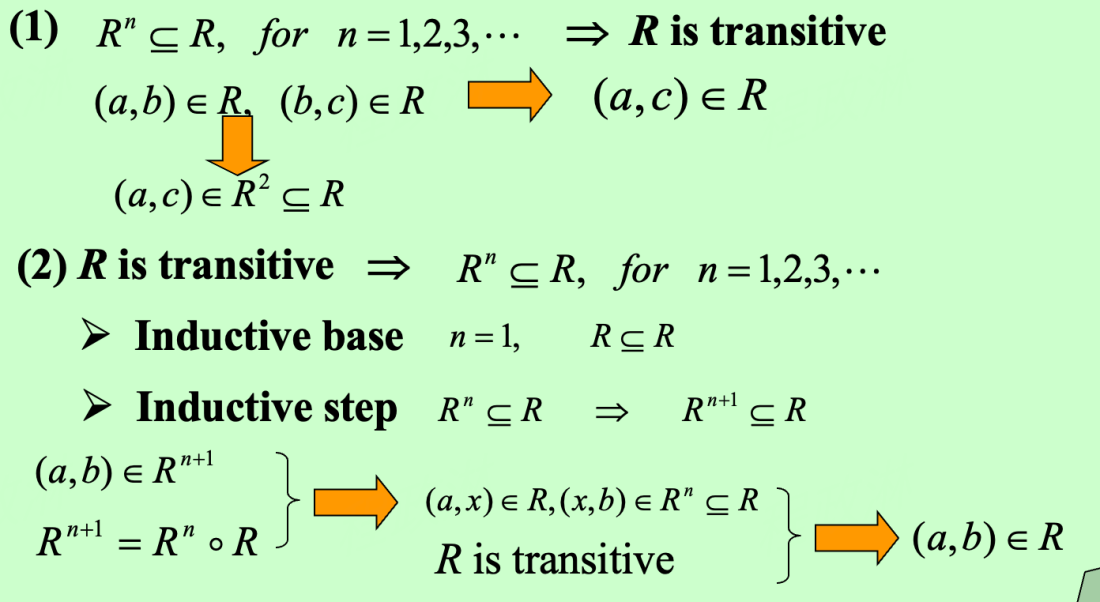
- [Theorem] The relation \(R\) on a set A is transitive iff \(R^n\subseteq R\), \(n=1,2,3,...\)
Proof
Inverse - \(R^{-1}\)¶
- \(R=\{ (a,b) \mid a \in A, b\in B,aRb \}\)
- \(R^{-1}=R=\{ (b,a) \mid (a,b)\in R, a \in A, b\in B,aRb \}\)
- 如何计算?
- 由定义直接计算
- 关系矩阵转置
Properties¶
- Suppose that \(R,S\) are the relations from \(A\) to \(B\)
- \(T\) is the relation from \(B\) to \(C\)
- \(P\) is the relation from \(C\) to \(D\)
- \((R\cup S)^{-1}=R^{-1}\cup S^{-1}\)
- \((\bar R)^{-1}=\bar{R^{-1}}\)
- \((R-S)^{-1}=R^{-1}-S^{-1}\)
- \((A \times B)^{-1}=B\times A\)
- \(\bar R = A\times B -R\)
- \((S\circ T)^{-1}=T^{-1}\circ S^{-1}\)
- \((R\circ T)\circ P = R\circ (T\circ P)\)
- \((R\cup S)\circ T=R\circ T\cup S\circ T\)
Closures of Relations (关系闭包)¶
- 定义:R 是集合 A 上的关系。R 可能具有或者不具有某些性质 P,例如自反性、对称性或传递性。如果存在包含R 的具有性质 P 的关系 S,并且 S 是所有包含 R 且具有性质 P 的关系的子集,那么 S 叫做 R 的关于性质 P 的闭包
- \(r(R)=R\cup I_A,\,I_A=\{(x,x)\mid x\in A\}\)
- \(R=R\cup I_A \Leftrightarrow R\) is reflexive
- \(s(R)=R\cup R^{-1}\)
- \(R=R\cup R^{-1}\Leftrightarrow R\) is symmetric
- 定义有向图的 path: A sequence of edges \((x_0,x_1),(x_1,x_2),...,(x_{n-1},x_n)\), denoted by \(x_0,x_1,...,x_{n-1},x_n\)
- 传递关系可以和有向图中的路径相对应
- circle/circuit: \(x_0=x_n\)
- \(\lvert A \rvert =n\), then any path of length\(\gt n\)must contain a cycle
- [Theorem] 在 \(A\) 上的关系 \(R\),存在 \(a\) 到 \(b\) 的长度为 \(n\) 的路径当且仅当 \((a,b)\in R^n\)
- The Connectivity Relation: 对 \(R^*\) 的任意 \((a,b)\),都存在一条从 \(a\) 到 \(b\) 的路径
- \(R^*= \bigcup_{n=1}^\infty R^n\)
- \(t(R)=R^*\)
- \(\lvert A \rvert =n\), then \(t(R)=R^*=R\cup R^2\cup ... \cup R^n\)
How to Compute t(R)?¶
- 时间复杂度为:\(O(n\cdot (n^3+n))=O(n^4)\)
🤔
Warshall 算法也即 Floyd-Warshall 🔗 算法,其中 Floyd 算法是求解多源最短路的算法,可以求出所有点之间的最短距离。Warshall 算法是 Floyd 的弱化版本,只关注最短路的存在性
- interior vertices (内部点):定义为一条路径除去起始和结尾的点,例如 \(a,b,c,d,e\) 的内部点是 \(b,c,d\)
- Warshall's Algorithm 通过构造 \(W_0,W_1,...,W_n\)矩阵来求解 \(t(R)\),其中 \(W_0=M_R,W_n=t(R)\)
- \(W_k\) 的定义是:对于 \(W_k\) 中的每一个 \(w_{ij}^{(k)}\),若存在一条从 \(v_i\) 到 \(v_j\) 的路径,且其内部点均在 \(\{v_1,v_2,...,v_k\}\) 中,那么 \(w_{ij}^{(k)}=1\),否则为 0
- \(W_k\) 可以由 \(W_{k-1}\) 计算,考虑两种情况:

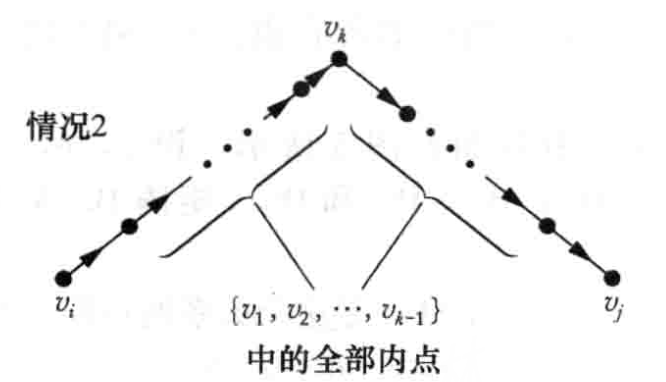
- 因此,从 \(W_{k-1}\) 计算 \(W_k\) 的方法是:\(w_{ij}^{(k)}=w_{ij}^{(k-1)}\vee(w_{ik}^{(k-1)}\land w_{kj}^{(k-1)})\),时间复杂度为 \(O(n^3)\)
- 从关系矩阵上来看,计算方法表现为要么 \(w_{ij}^{(k-1)}\) 为 1,要么从对角线扫描行列,确定是否同时 1(如下图 红线 所示)
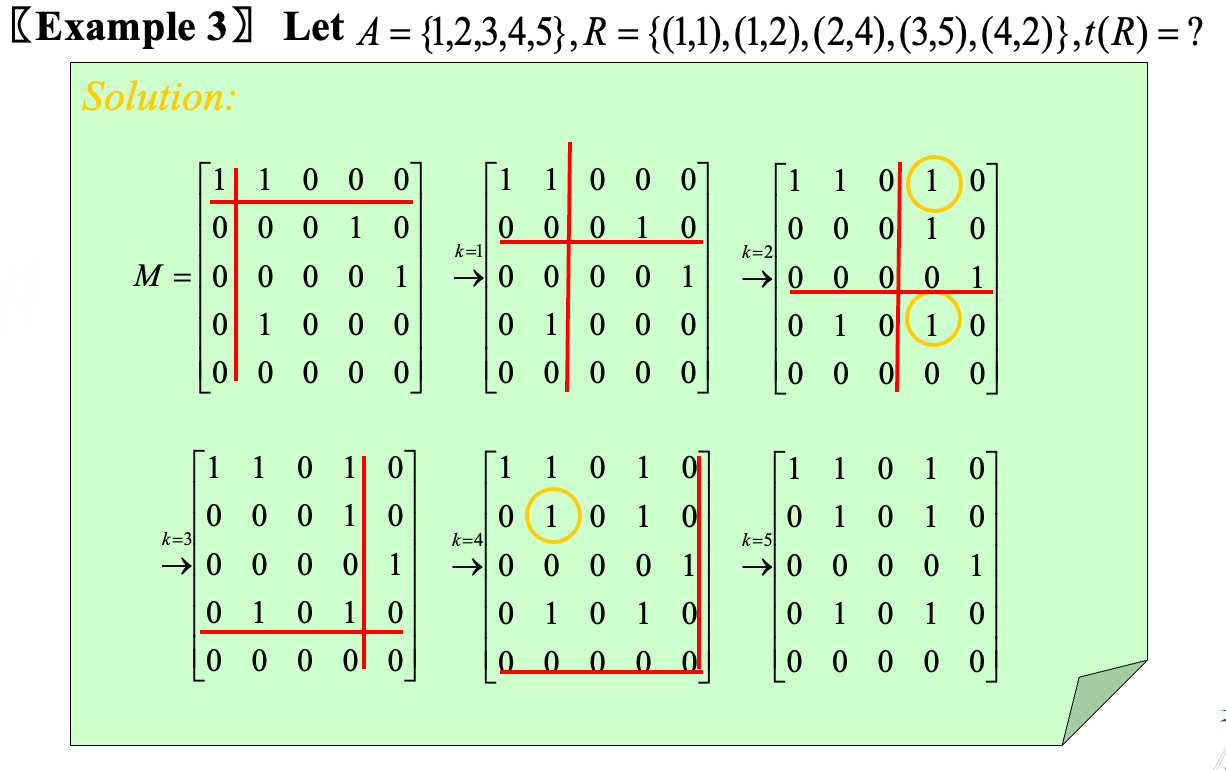
一个例子
Equivalence Relations¶
- Definition: reflexive & symmetric & transitive
- \(a \sim b\): \(a\) and \(b\) are equivalent
- \(\left[ x \right]_R ,\, \left[ x \right]\): the equivalence class of \(x\)
- Theorem \(R\) is an equivalence relation on a set \(A\), then \(aRb\Leftrightarrow \left[ a \right] = \left[ b \right] \Leftrightarrow \left[ a \right] \cap \left[ b \right] \neq \varnothing\)
Partitions¶
- Partition (划分) 即将一个集合划分为两两互不相交的非空子集,其并集为原集
- 集合的划分和等价类一一对应
- 划分、等价类在关系图中的体现为不同的连通分量
等价关系计数¶
- Bell 数:\(n\)元集合上等价类的个数 🔗:\(B_{n+1}=\sum_{k=0}^nC(n,k)B_k,\, B_0=1,B_1=1,B_2=2\)
- 手算类似帕斯卡三角形:
- 将 1 放在其第一个位置
- 每行三角形中最左边的值通过复制上一行中最右边的值。每行中的其余位置是左侧和左上方位置的两个值之和
- \(n\) 元集合上分成 \(k\) 个等价类的个数:\(S(n,k)\),第二类斯特林数
- \(S(n,k)=S(n-1,k-1)+k\cdot S(n-1,k),\,\,S(0,0)=1,\, S(k,0)=0\, (k>0)\)
- 手算先分组,再求组合数。例如 \(S(5,3)\),分为 2 2 1, 3 1 1。然后分组求排列,和球盒模型中球不相同,盒子相同等价
Properties¶
- \(R_1,R_2\) are equivalence relations on \(A\), then \(R_1\cap R_2\) is equivalence relation on \(A\)
- \(R_1,R_2\) are equivalence relations on \(A\)
- then \(R_1\cup R_2\) is reflexive and symmetric, not transitive
- \((R_1\cup R_2)^*\) is equivalence relation on \(A\)
- \(R_1\oplus R_2\) 永远都不是等价关系,因为不 reflexive
Partial Orderings¶
- Definition: reflexive & antisymmetric & transitive
- \((S,R)\): set of partial order \(R\) on set \(S\), called partially ordered set or poset
- \(a\preceq b\):\((S,R)\)is a poset, \((a,b)\in R\)
- Comparable: \(a,b\) of \((S,\preceq)\), \(a\preceq b\)or\(b \preceq a\)
- Incomparable: \(a,b\) of \((S,\preceq)\), neither \(a\preceq b\) nor \(b \preceq a\)
- 任意两个元素之间 Comparable 时:\(S\)is called totally ordered or linearly ordered set, \(R\) is called linear order (线序) or total order (全序), \((S,R)\) is called chain (链)
- 有 \(n!\) 种
- \(n\) 元集合上的偏序计数
- OEIS A001035 🔗
- 1, 3, 19, 219
Lexicographic Order (字典序)¶
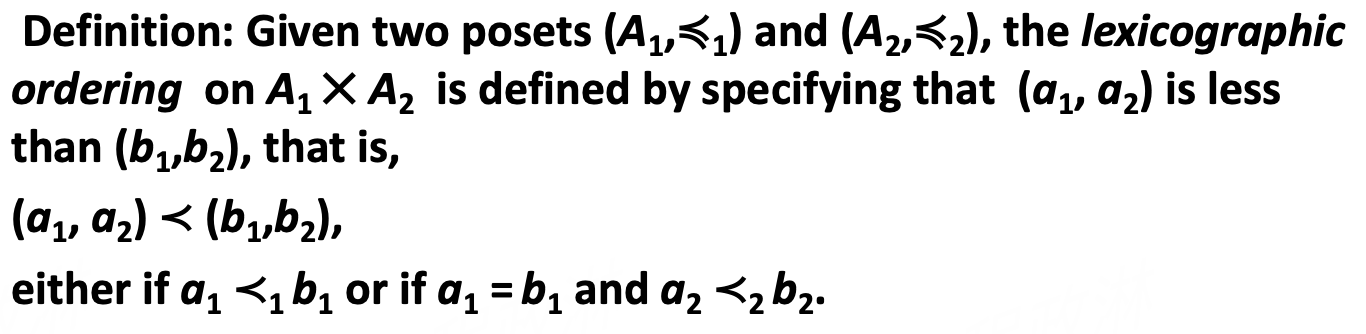
Hasse Diagram (哈斯图)¶
Example
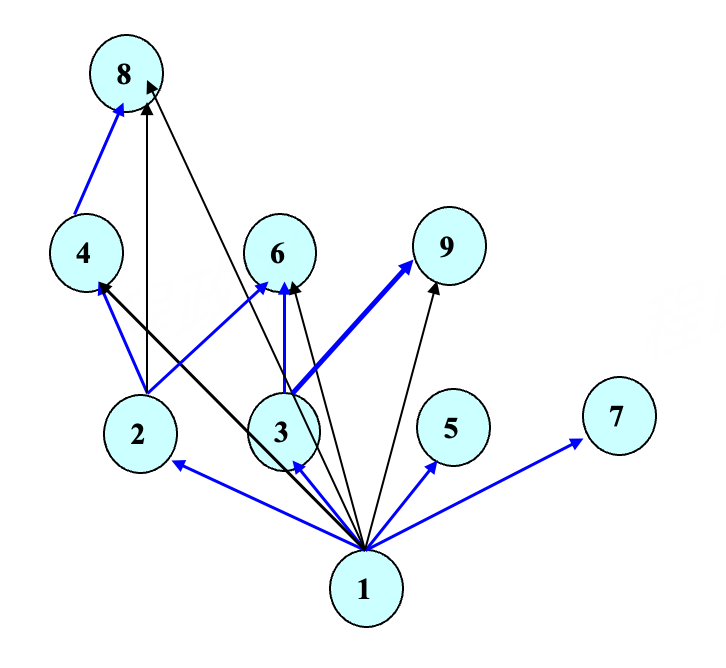
- \(A=\{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9\}\), \(R=\{(a,b)\mid a | b,a,b \in A\}\)
- 用有向图表示出所有的关系
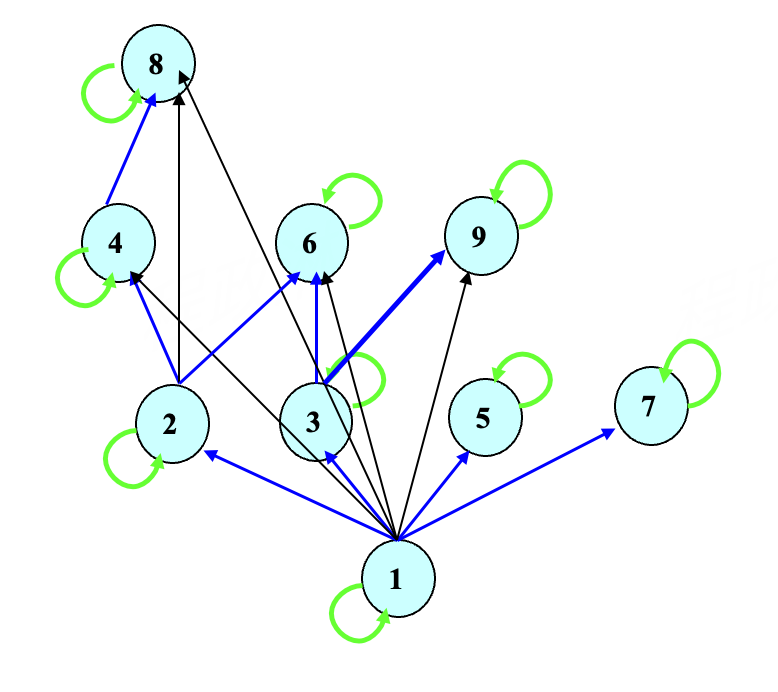
- 删除自环
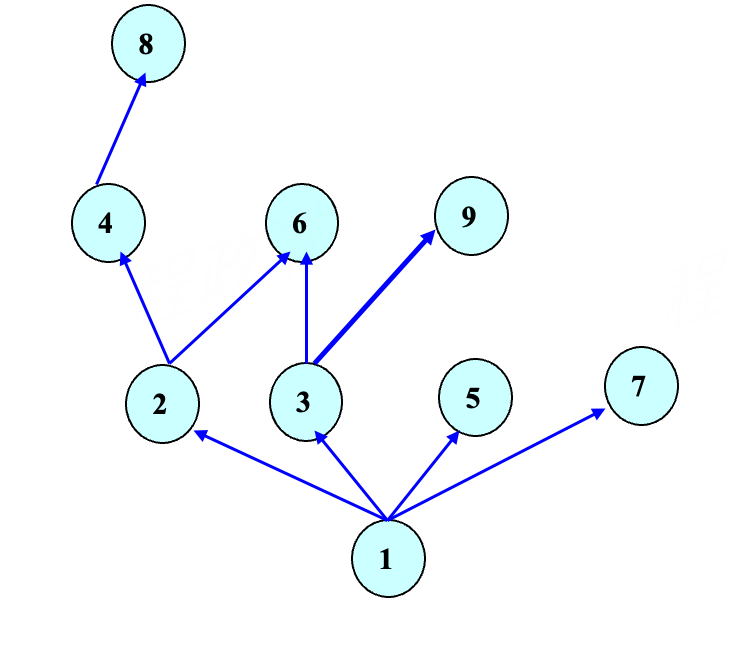
- 删除可以通过传递性得到的边
- 转为无向图
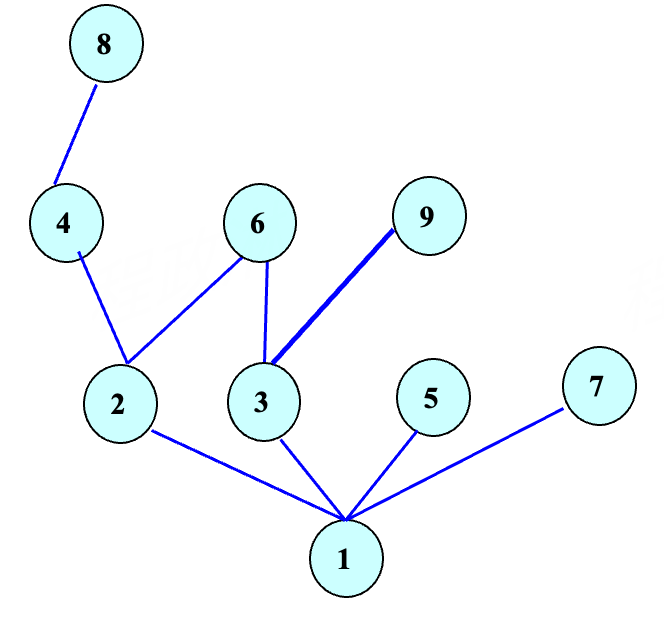
chain and antichain¶
- totally ordered set \(\Leftrightarrow\) chain (任意两个元素可以比较)
- antichain (任意两个不同元素都不可比较)
- 例如 30 的因数整除关系,\(\{1,2,6,30\}\) 是一个 chain,\(\{ 2,3,5 \}\) 是 antichain
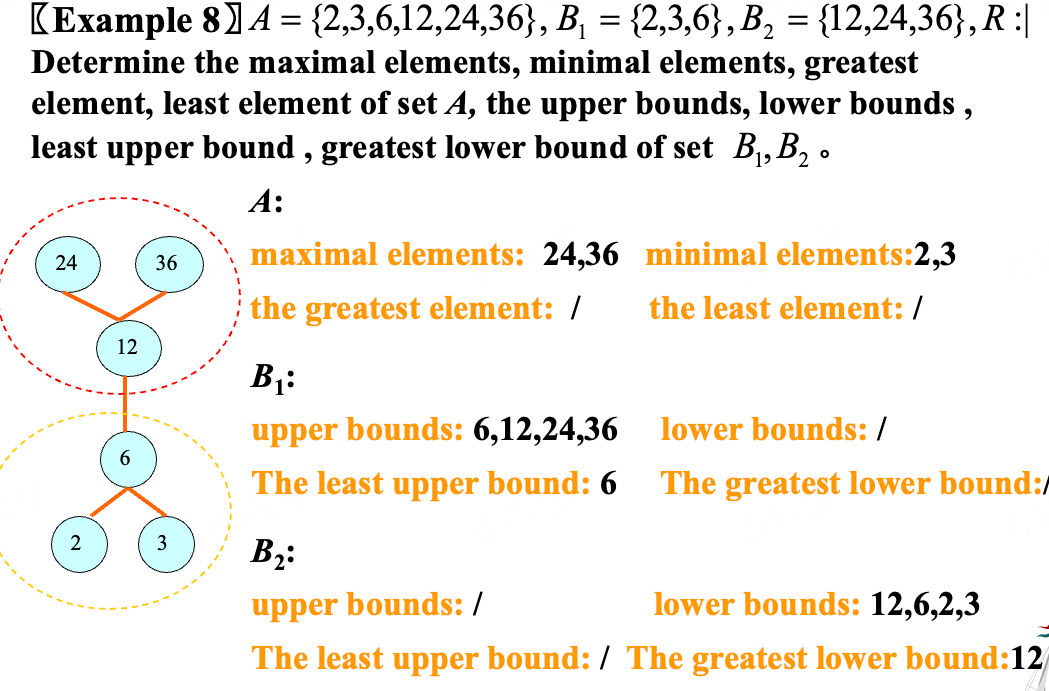
Maximal and Minimal Elements (极大值、极小值)¶

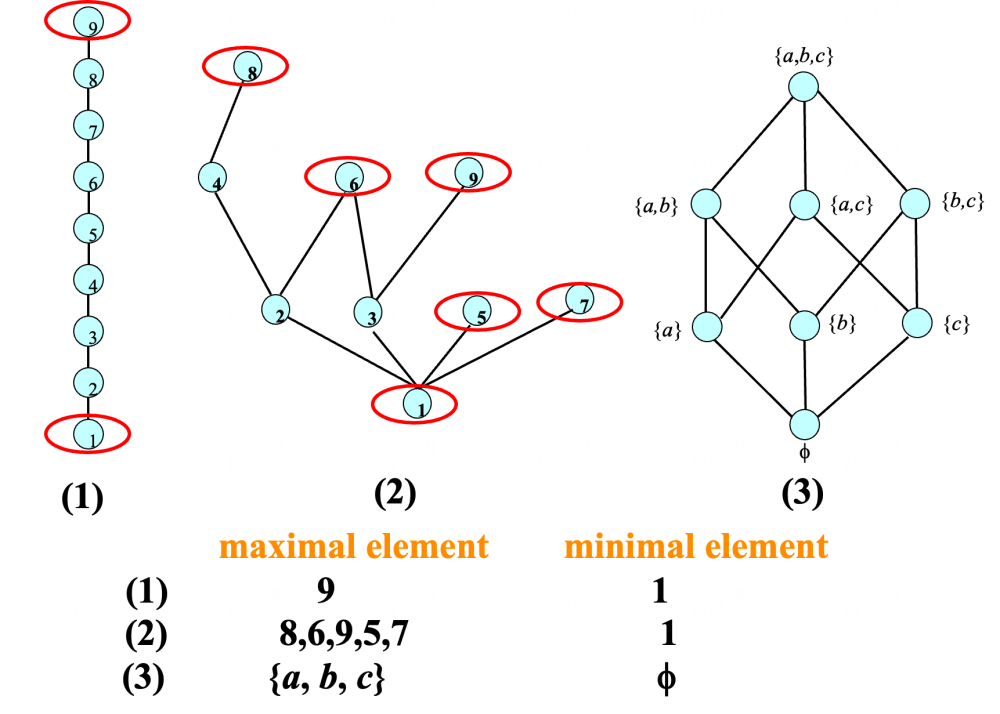
Greatest and Least Element (最大值、最小值)¶
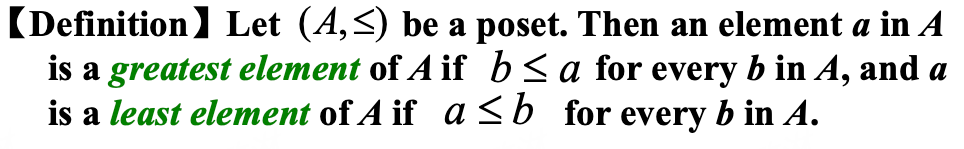
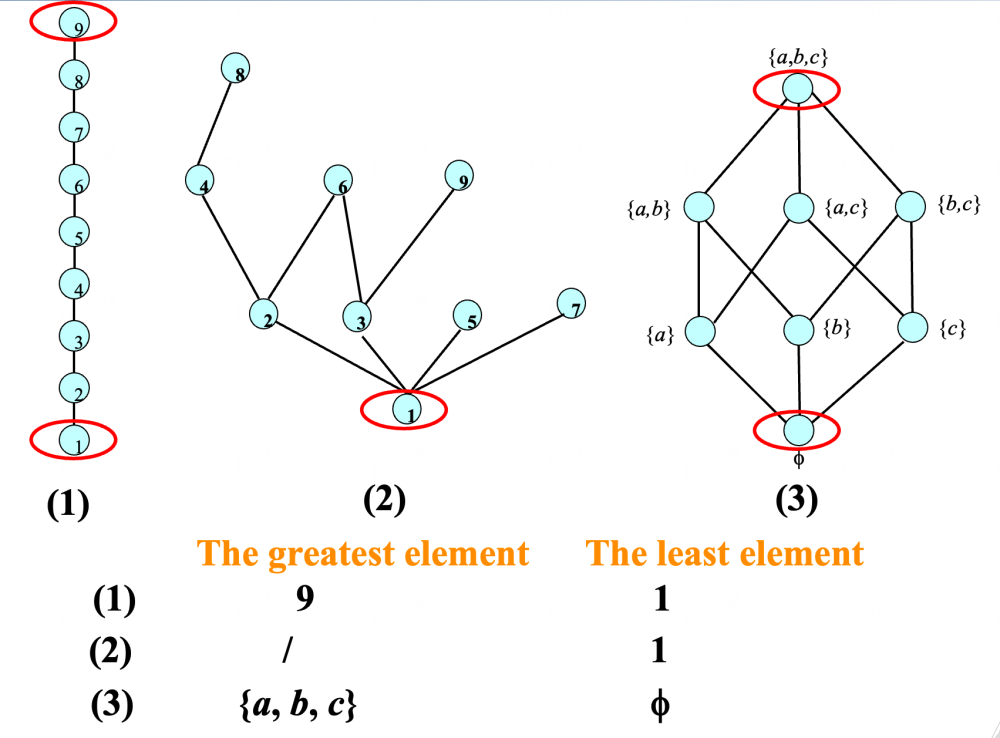
- 最大值、最小值如果存在,那么是唯一的
Upper and Lower Bounds (上、下界)¶

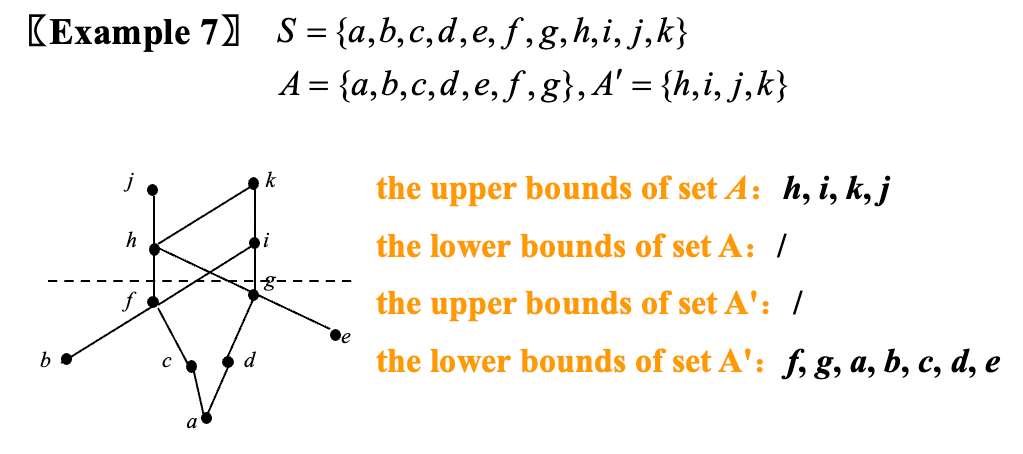
Least Upper and Greatest Lower Bounds (最小上界、最大下界)¶

Well-ordered Sets (良序集)¶
- well-ordered \(\Rightarrow\) totally ordered (良序推全序)
Lattices (格)¶
- 每对元素 都有 最小上界 和 最大下界 称为「格」
- totally ordered \(\Rightarrow\) 格
- \((\mathbb{Z},\ge )\)
- \((\mathbb{Z^+},\mid)\) (glb 为 \(\gcd\),lub 为 \(\operatorname{lcm}\))
- \((\mathcal{P}(s),\subseteq)\) (\(A,B\subseteq S\), glb 为 \(A\cap B\), lub 为 \(A\cup B\))
- \((\mathcal{P}(s),\supseteq)\) (\(A,B\subseteq S\), glb 为 \(A\cup B\), lub 为 \(A\cap B\))
- \((S, R)\) 为格,则 \((S,R^{-1})\) 也是格
Topological Sorting¶
- 从一个偏序构造一个全序
- 每次找一个极小元素,然后删除该元素和与其相关联的关系后,继续寻找极小元素,直到形成全序